Growth and characterization of lipid nanosystems. On this examine, VitE:SM nanosystems had been proposed as a method to focus on TAMs within the liver to deal with pancreatic most cancers metastasis. As talked about within the introduction, some of these nanocarriers have demonstrated vital potential for delivering therapeutic brokers to deal with most cancers [34], and have confirmed able to penetrating dense most cancers spheroids, particularly in pancreatic most cancers [36, 57]. Likewise, VitE:SM nanoemulsions have proven preferential biodistribution to the liver, and the function of VitE and SM in modulating irritation has been beforehand described [46, 47]. The formulated compositions had been ready by adapting an ethanol injection methodology, enabling a single-step preparation and the easy formation of the nanosystems [34, 35, 37] (Fig. 1a). Sphingomyelin (SM) consists of two lengthy carbon chains (hydrophobic tail), a secondary amine group appearing as a linker and a phosphate group (hydrophilic head). Contemplating its lipophilicity, it’s anticipated that it could type emulsions when mixed with oils comparable to Vitamin E (VitE), a undeniable fact that has been validated experimentally and thru computational simulation research [34]. Various oils may also type nanoemulsions, together with SM, following the identical rational and experimental strategy. The nanoemulsion compositions is also complemented by further phospholipids, together with Phosphatidylcholine (PC), Phosphatidylinositol (PI), Phosphatidylserine (PS), Phosphatidylglycerol (PG), or Palmitic acid (PA), since there’s rising proof suggesting that sure phospholipids can affect TAM reprogramming [58, 59]. Consequently, the hydrophobic carbon chain may be included into the oily core of the construction, whereas the hydrophilic phosphate head is uncovered on its floor.
Thus, VitE:SM nanoemulsions and different compositions had been formulated for comparative functions, as detailed in Fig. 1b and Desk 1. Following formation, all formulations confirmed acceptable physicochemical properties, with minor variations in measurement and floor properties, rendering homogeneous populations. By way of colloidal stability, the formulations had been saved at 4°C, and their physicochemical properties, comparable to particle measurement, inhabitants homogeneity (PDI) and zeta potential had been monitored over time. Formulations containing VitE, both with SM or PC (1:0.1 w/w), remained secure for no less than 30 days (Determine S1a-b), in settlement with earlier outcomes displaying excessive stabilities for VitE:SM nanoemulsions [34].
Subsequently, the lipid nanosystems had been incubated with full RPMI cell tradition medium supplemented with 1% FBS at 1:6 (v/v) and measured for as much as 24 h at 37°C underneath orbital shaking. Their measurement and PDI had been decided at completely different time factors by additional diluting the pattern in ultrapure water at 1:10 (v/v). Consistent with the outcomes, all formulations confirmed a superb stability with minimal improve in particle measurement and polydispersity over time (Determine S1c-k).
The lipid nanosystems comprising VitE:SM display probably the most favorable M2 macrophage reprogramming capability. Since our major goal was to reprogram macrophages with nanotechnology, we first assessed the conduct of VitE:SM nanoemulsions in relation to nanosystems with completely different lipid compositions (Fig. 1b, Desk 1) in immortalized murine bone-marrow-derived macrophages (muIBMDM) [60] to find out their potential toxicity and affect on M2 macrophage reprogramming.
IBMDM macrophages had been polarized for twenty-four h with LPS + IFN-γ for M1 polarization and IL-4 to induce M2 polarization. IL-4 is the commonest cytokine used to polarize macrophages to an M2 state [61,62,63]; nevertheless, you will need to notice that M2 polarization of macrophages is co-regulated by a wide range of cytokines and chemokines launched by PDAC cells and CAFs within the TME [15]. Following polarization, M2 macrophages had been handled with nanoemulsions for 4 h to evaluate toxicity and reprogramming by qRT-PCR evaluation after a 24-h post-treatment interval, and by Western blotting to judge the expression of the principal M2 marker Arg1 at 48 h post-treatment (Fig. 2a). To evaluate related toxicity induced by the completely different formulations, a bioluminescent assay that measures the discharge of adenylate kinase from broken cells was employed, revealing that VitE:SM was one of many least cytotoxic formulations (Fig. 2b), which was confirmed by mild microscopy (Determine S2a). VitE:OA:SM was discarded due the excessive cytotoxicity noticed (Determine S2a).
The particular lipid composition of the nanosystems has an affect on M2 macrophage reprogramming. a Experimental design for macrophage polarization and therapy with the lipid nanosystems: murine immortalized bone marrow-derived macrophages (IBMDM) had been induced to an M1 phenotype utilizing LPS (10 ng/mL) + IFN-γ (10 ng/mL) or to an M2 phenotype with IL4 (10 ng/mL) for twenty-four h. Following polarization, lipid nanosystems (1 mg/mL) had been incubated with macrophages for a 4-h length: VitE:SM, M:SM, VitE:PC, VitE:SM:PI, VitE:SM:PS, VitE:SM:PG, and VitE:SM:PA at completely different concentrations of PA. Subsequently, IBMDM cells had been washed and cultured in RPMI medium for qRT-PCR and toxicity assays for twenty-four h, or Western blot analyses for 48 h. b Fold change in relative luciferase exercise (i.e., toxicity) ± SD decided in IBMDM cultures handled with the indicated completely different nanoemulsion compositions in comparison with untreated M2 polarized macrophages, set as 1.0 (n = 3). c Evaluation of the degrees of the principal M2 marker Arg1 by qRT-PCR. Bars signify the imply fold change ± SD (n = 3), with untreated M2 set as 1.0. d High: Consultant Western immunoblots of ARG1 protein expression ranges. Backside: Densitometric evaluation of the immunoblots is represented within the bar diagram. Bars signify the imply fold change ± SD (n = 4), with untreated M2 set as 1.0. e Abstract desk of three parameters chosen for evaluating the perfect nanoemulsion composition. For toxicity, low < 4 AU, medium = 4–7 AU, excessive > 7 AU. ∗ = p < 0.05; ∗ ∗ = p < 0.01; ∗ ∗ ∗ = p < 0.001; ∗ ∗ ∗ ∗ = p < 0.0001; ns = not vital. One-way ANOVA take a look at for a number of comparisons with Dunnett’s put up hoc take a look at, in comparison with the untreated M2 pattern
Relating to reprogramming in direction of a extra M0/M1 phenotype, qRT-PCR and Western Blot evaluation of Arginase 1 (Arg1/ARG1) expression, a widely known marker for M2 macrophages in PDAC [64] was carried out (Fig. 2a). By qRT-PCR evaluation we noticed a common lower in Arg1 expression with all of the examined formulations, with a extra pronounced lower noticed within the case of the VitE:SM formulation in comparison with untreated M2 macrophages (Fig. 2c). This pattern was equally noticed on the protein stage. Whereas a lower in ARG1 expression was achieved with almost all of the formulations, it was solely statistically vital within the case of nanoemulsions containing VitE:SM and VitE:SM:PI (Fig. 2d).
Based mostly on these knowledge, we decided that the best formulation for macrophage reprogramming and probably the most appropriate low poisonous composition for additional improvement was the nanosystem containing VitE:SM (Fig. 2e). To analyze the potential synergies provided by VitE and SM in TAM reprogramming, we performed a further experiment by which IBMDM macrophages had been first polarized with IL-4 for twenty-four h to induce M2 polarization. The M2 macrophages had been then handled for 4 h with the VitE:SM nanoemulsions, SM, VitE, or a free mixture of VitE and SM to evaluate toxicity (% reside cells) and M2 reprogramming through circulate cytometry (CD45 + < CD11b + < F4/80 + < CD206 +) 24 h post-treatment (Determine S2b). Our outcomes affirm that the VitE:SM nanoparticle composition displays a synergistic impact to reprogram M2 TAMs and demonstrates improved cell viability in comparison with the opposite compositions. To additional analyze the construction of this composition, we employed area emission scanning electron microscopy (Determine S3).
We then investigated whether or not major murine macrophages derived from major bone marrow monocytes (BMDM) handled with VitE:SM maintained their reprogramming over time and whether or not these results had been reversible upon subsequent publicity to the M2-polarizing cytokine IL-4 (Determine S4a). Certainly, Western blot evaluation of ARG1 revealed a continued discount of this M2 marker over time in BMDMs handled with the VitE:SM nanosystem. Moreover, VitE:SM nanoemulsion-treated macrophages that had been repolarized with IL-4 didn’t improve ARG1 to ranges noticed in management teams (Determine S4b). Contemplating the implications for in vivo use, these findings counsel that regardless of the continual affect from tumor secreted pro-TAM elements, handled macrophages are more likely to retain the polarization state induced by the VitE:SM nanoemulsions over time; nevertheless, as said above, M2 polarization of macrophages in vivo is co-regulated by a wide range of cytokines and chemokines launched by PDAC cells and CAFs within the TME [15].
We hypothesized that the potent reprogramming capability of the VitE:SM formulation arises from two key properties. On the one hand, it’s well-established that the phagocytosis of lipid membranes by macrophages impacts their programming and metabolism [32, 65, 66]. Some research make the most of cell membrane-derived nanoparticles (nanoghosts) for macrophage reprogramming, attributing this impact to parts like cytokines and chemokines current within the cell membranes of nanoghosts. Nevertheless, it’s also believable that membrane sphingolipids comparable to SM play an important function in macrophage reprogramming [44,45,46,47, 66]. Then again, the immunostimulant properties of VitE might also contribute to macrophage reprogramming [40,41,42]. Thus, the twin actions of VitE and SM suggests a possible synergy in enhancing the reprogramming capability of this composition, making this mix notably promising for additional experimentation.
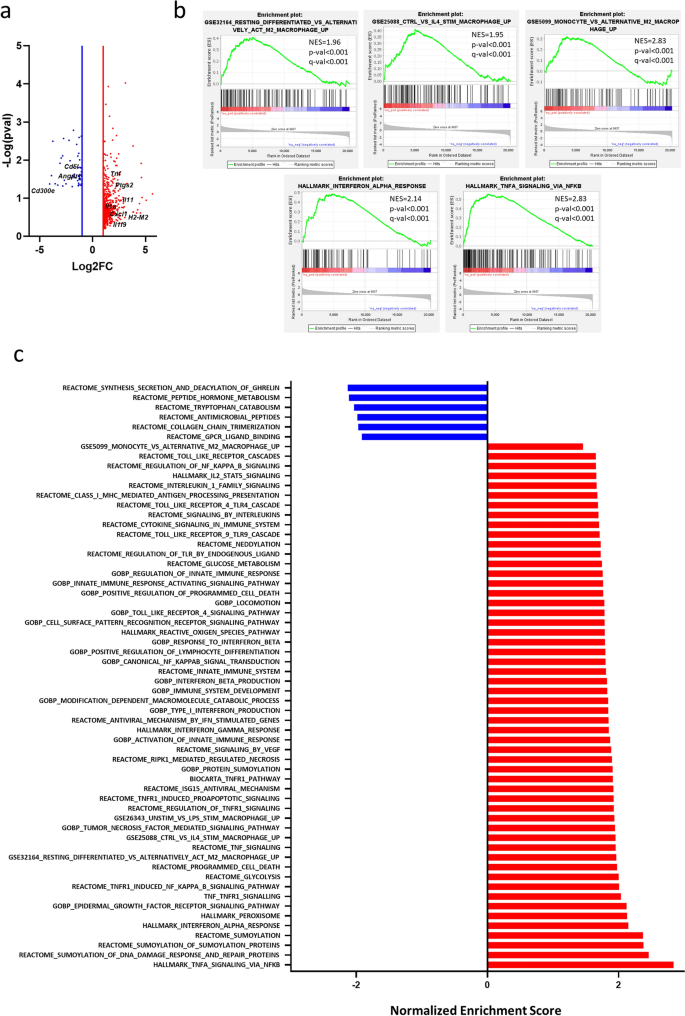
RNAseq evaluation of M2 and M2 VitE:SM nanoemulsion-treated macrophages. To additional examine the consequences of the VitE:SM formulation on M2 macrophage polarization on the transcriptomic stage, we carried out RNAseq on IL-4-stimulated (M2) and IL-4-stimulated VitE:SM nanoemulsion-treated muBMDMs. Among the many genes considerably upregulated in VitE:SM-treated macrophages, we discovered genes associated to irritation (i.e., Tnf, Ptgs2, Il-11, Il-1a, Cxcl1) and with antigen presentation (i.e., H2-M2). Moreover, among the many downregulated genes, we recognized Cd51 and Cd300e, that are associated to M2 polarization, and Angpt1 which is a pro-angiogenic issue (Fig. 3a).
RNAseq evaluation of M2 and M2 VitE:SM nanoemulsion-treated macrophages. a Volcano plot displaying differentially expressed genes in VitE:SM nanoemulsions-treated (1 mg/mL) M2 macrophages versus naïve M2 macrophages. Crimson dots, genes upregulated; blue dots, genes downregulated. Genes of have been labelled in black. b Gene set enrichment evaluation (GSEA) plots displaying a major enrichment within the indicated gene signatures for VitE:SM nanoemulsions-treated M2 macrophages. Normalized enrichment rating (NES) and p- and q- values are indicated for every plot. c Histogram illustration of the NES of considerably altered gene signatures down- (blue) and upregulated (pink) in VitE:SM-treated M2 macrophages
We subsequent carried out a Gene Set Enrichment Evaluation (GSEA) using Molecular Signature Database (MsigDB) signatures (together with Gene Ontology, Reactome and Hallmarks) or customized gene signatures. Curiously, VitE:SM nanoemulsion-treated macrophages recuperate a sample associated to resting differentiated macrophages or monocytes, slightly than a gene set related to M2 or IL-4 stimulated macrophages. We additionally discovered primarily an enrichment in gene signatures associated to TNF-TNFR1 signaling, but additionally macrophage activation through Toll receptors, interferon-related signaling, reactive oxygen species and signatures associated to innate immune system activation, indicating that VitE:SM therapy induces a reprogramming of M2 macrophages in direction of a extra inflammatory and fewer immunosuppressive phenotype, which is in step with our earlier outcomes and speculation (Fig. 3b-c).
The intraperitoneal injection of VitE:SM nanoemulsions reduces tumor burden in an orthotopic KPC tumor mannequin. To initially validate the in vivo efficacy of the nanosystems, we performed a preliminary examine using murine PDAC cells obtained from spontaneous tumors from the KPC (LSL-KrasG12D/+; LSL-Trp53R172H/+; Pdx-1-Cre) mouse mannequin [67]. These cells had been orthotopically injected into the pancreas of syngeneic and immunocompetent C57BL/6 wild-type (WT) mice (Fig. 4a), with the nanosystem therapy commencing on the seventh day post-implantation in two distinct non-parallel experiments. In every experiment, randomized teams of 4 or 5 mice had been intraperitoneally injected with a automobile resolution (0.9% NaCl) for the management mice or 69 mg/kg of VitE:SM nanoemulsions for handled mice. This routine was utilized for 5 consecutive days per week. Mice had been euthanized on day 27 post-implantation, after confirming tumor development in a sentinel mouse by Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) (Determine S5a). Complete physique weight was recorded at first and finish of the therapy to evaluate nanoemulsion toxicity, revealing no variations between teams all through the examine interval (Fig. 4b). On this mannequin, tumor presence sometimes impairs weight acquire and sometimes results in lowered meals consumption or tumor-associated cachexia, so the dearth of weight acquire is anticipated. Full-body necropsy was then carried out and no liver toxicity was noticed on the organotypic stage (Fig. 4c), nor had been variations noticed in liver weight (Fig. 4d). On the histopathological stage, examination of H&E-stained liver slides confirmed that the construction and structure of the liver remained unaffected by the therapy. There was no proof of irritation, necrosis, or lack of structure within the central vein or sinusoids. (Fig. 4e). Lastly, the evaluation of liver toxicity following therapy with VitE:SM nanoemulsions, as decided by liver perform assessments, didn’t reveal elevated values of ALT, AST and GGT when in comparison with commonplace reference ranges (Desk S3). Liver toxicity was additionally absent in non-implanted mice handled with three doses of VitE:SM nanoparticles administered each two days over a one-week interval. Serum evaluation after multiples remedies confirmed regular ALT enzyme ranges, with no vital distinction between management and VitE:SM-treated mice (Determine S5b). Moreover, the mice didn’t expertise weight reduction throughout the therapy course of (Determine S5c). This underscores the biocompatibility of the chosen nanosystem, as evidenced by the absence of toxicity related to the nanoemulsion. Furthermore, not like different remedies that deplete TAMs, comparable to clodronate or toxin-conjugated monoclonal antibodies [31, 68], VitE:SM nanosystems might provide a safer therapeutic possibility.
Intraperitoneal injection of VitE:SM nanoemulsions reduces tumor burden in an orthotopic KPC tumor mannequin. a Experimental set-up for the in vivo syngeneic mannequin in C57BL/6 mice. Mice had been orthotopically implanted with 2,500 KPC cells/pancreas and therapy was initiated 7 days post-implantation, receiving VitE:SM nanoemulsions remedies (69 mg/kg) 5 days per week for 3 weeks through intraperitoneal (IP) injection. b Fold change ± SD of the full weight of the animals at first and completion of the therapy. The preliminary weights for the management (n = 10) and VitE:SM (n = 9) teams from two unbiased experiments had been pooled and every set as 1.0 to watch the burden evolution all through the experiment. Days post-implantion (DPI). c Consultant photographs of the liver on the experimental endpoint from management (n = 10) and VitE:SM-treated (n = 9) teams from two unbiased experiments. Scale = 1cm. d Liver weight from c. Information had been normalized for every unbiased experiment (n = 2) with the bars representing the imply fold change ± SD, with the management set as 1.0. Unpaired t take a look at. ns = not vital. e Consultant photographs (40X) of H&E-stained liver slices on the experimental euthanize time level from management or VitE:SM-treated mice. Scale = 400µm. Zoom areas are depicted inside squares. Scale = 100µm. CV Central vein, S Sinusoids. f Consultant photographs of the tumor (T) and adjoining peritoneum tumor-derived plenty (PM) on the experimental endpoint for management (n = 10) and VitE:SM-treated (n = 9) teams from two unbiased experiments. A further management group handled with non-effective nanoparticles M:SM (n = 4) was included. All tumor photographs are offered in Determine S6. Scale = 1cm. S = Spleen served as an anatomical reference for the pancreas. g Fold change in T + adjoining PM weight ± SD from f. Information had been normalized for every duplicate experiment with the management set as 1.0. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s put up hoc take a look at, in comparison with management. ∗ ∗ = p < 0.01. ns = not vital
Each on the stage of the tumor alone (Determine S5d) or together with the adjoining peritoneal tumor-derived plenty (Fig. 4f-g), a discount in complete tumor weight was evident in mice handled with the VitE:SM nanosystem in comparison with the management group (Fig. 4f-g and S6). Importantly, and to particularly spotlight the exercise of the VitE:SM formulation, a further nanoemulsion management group was included. Particularly, mice had been additionally handled with Mygliol (M):SM nanoemulsion, which had been proven to be much less efficient on the stage of M2 TAM reprogramming (Fig. 2). Tumor weights confirmed a major lower in tumor burden with intraperitoneal administration of VitE:SM nanoemulsions however not with the M:SM nanoparticles (Determine S5d and 4g), indicating that the VitE:SM formulation has particular anti-tumoral properties.
Taken collectively, these findings align with different research which have additionally utilized nanoparticles to modulate the immune system; nevertheless, the composition of the nanoemulsion seems to be essential to attain an anti-tumor impact. Thus, the combination of nanotechnology to reinforce immune responses and/or have an effect on tumor development represents a rising and constant pattern and highlights the efficacy of nanoparticle-based approaches in immuno- and tumor modulation [69, 70].
Focusing on capability of the TopFluor® (TF)-labelled VitE:SM nanoemulsions in vitro and in vivo. To additional consider the in vivo utility of the nanosystems, nanoemulsions had been formulated utilizing SM labeled with the inexperienced fluorophore TopFluor® (TF) for monitoring functions in mice (Fig. 5a and Desk 2). First, confocal microscopy photographs of IBMDM macrophages revealed inexperienced fluorescence in these cultures handled with VitE:SM:TF nanoemulsions (Fig. 5b). Detection of the fluorophore by circulate cytometry, utilizing Ex488nm Em530/30nm, confirmed almost full staining of macrophages (Fig. 5c). Because the aim of this examine was to focus on liver TAMs, we assessed which route of administration would favor liver biodistribution, as measured by circulate cytometric evaluation of tumors, liver and lungs. VitE:SM:TF nanoemulsions had been administered intraperitoneally or retro-orbitally to KPC orthotopically implanted C57BL/6 mice seven days post-surgery, at a dose of 25 mg/kg of VitE:SM:TF nanoemulsions. Mice had been euthanized 48 h later to evaluate TF biodistribution within the tumor and the 2 principal organs prone to develop metastasis: liver and lungs. Following organ digestion, we confirmed by circulate cytometry that whereas intraperitoneal administration is perfect for reaching the tumor, retro-orbital injection is more practical in reaching the liver and the lungs (Fig. 5d). To additional examine retro-orbital injection with one other intravenous route, comparable to tail vein injection, we performed a further biodistribution experiment, which confirmed that retro-orbital injection was extra environment friendly in delivering the therapy to the liver, the first goal organ of this examine (Fig. 5e). To find out the kinetics of VitE:SM:TF nanoemulsion liver focusing on, and particularly liver macrophage (i.e., CD45 + , CD11b + , and F4/80 +) focusing on (Fig. 5f), VitE:SM:TF fluorescence was assessed 1 h, 4 h, 24 h, and 72 h put up retro-orbital injection. Movement cytometry evaluation of digested livers indicated that peak accumulation of VitE:SM:TF in liver macrophages was reached at 24 h, with a lower at 72 h (Fig. 5g). Thus, we established that the optimum therapy routine for subsequent in vivo intervention research to be retro-orbital injection each 48 h.
Focusing on capability of the TopFluor® (TF) labelled VitE:SM nanoemulsions in vitro and in vivo. a TopFluor® was included within the surfactant (TopFluor®-labelled-sphingomyelin) and injected within the aqueous part as beforehand defined (Fig. 1a). VitE:SM:TF = Vitamin E + TopFluor®-labelled-sphingomyelin nanosystem. b Confocal photographs of muBMDM cells handled or not with TF-labelled nanoemulsions (VitE:SM:TF, 0.5 mg/mL). Scale bar = 20 µM. DAPI: blue, TF: inexperienced. c Cytometry dot plots of muIBMDM cells within the presence or absence of VitE:SM:TF (0.5 mg/mL) nanoemulsions. Murine IBMDMs containing VitE:SM:TF nanoemulsions had been detected at a wavelength of Ex488 nm Em530/30 nm. SSC-A: Facet Scatter (Space). d Movement cytometry evaluation of the proportion of TopFluor®-positive reside cells ± SD in three completely different organs (liver, tumor, and lung) underneath two therapy modalities: intraperitoneal or retro-orbital (n = 2 mice per therapy). e Movement cytometry evaluation of the proportion of TopFluor®-positive reside cells ± SD within the liver underneath two intravenous therapy modalities (tail vein injection or retro-orbital) in comparison with management (n = 5 management, n = 5 mice per every therapy). ∗ = p < 0.05; ∗ ∗ ∗ = p < 0.001. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s put up hoc take a look at, in comparison with the retro-orbital situation. f Schematic illustration of the markers used to determine macrophages: CD45 + , CD11b + and F4/80 + . g Movement cytometry evaluation of the proportion of macrophages (CD45 + , CD11b + and F480 +) ± SD focused by the VitE:SM:TF nanoemulsions over time, with knowledge collected at 1 h, 4 h, 24 h and 72 h. Unpaired t take a look at evaluating 24 and 72 h. ns not vital
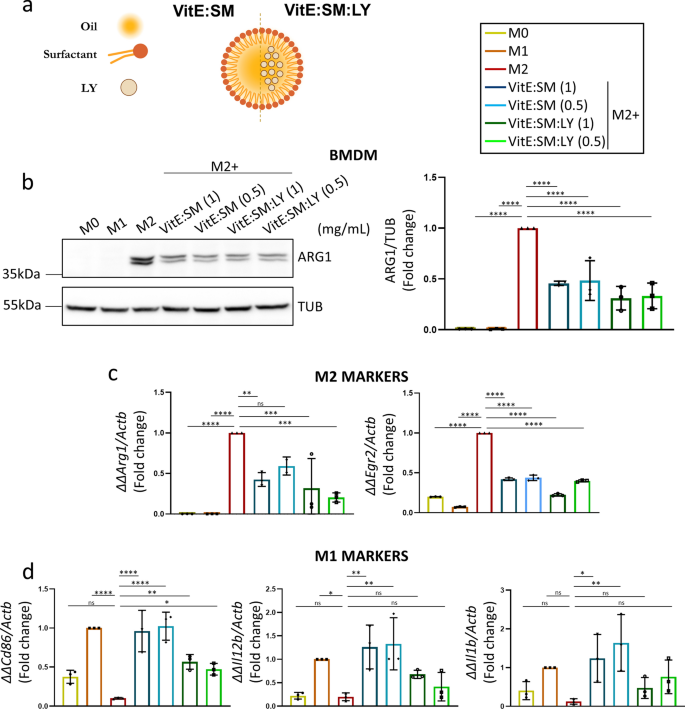
Loading of VitE:SM nanoemulsions with the TGF-βR1 inhibitor (LY2157299) reduces tumor development and diminishes TAM liver infiltration. Subsequent, we determined to additional discover the potential of VitE:SM nanoemulsions to encapsulate and ship the TGF-βR1 inhibitor Galunisertib LY2157299, known as LY (VitE:SM:LY) (Fig. 6a and Desk 2). We hypothesized that LY would inhibit the exercise of fibrotic cytokines in vivo and stop the M2 polarization of macrophages through TGF-β [71,72,73], as beforehand mentioned, thereby additional obstructing the formation of the pre-metastatic area of interest within the liver [48,49,50]. Furthermore, the encapsulation of LY into the VitE:SM nanosystem ought to in principle improve its supply and mitigate non-specific toxicity typically related to the administration of free LY [74, 75]. We first examined the VitE:SM and VitE:SM:LY compositions at completely different concentrations (1 and 0.5 mg/mL) in muBMDM cells polarized to an M2 state with IL-4. Western blot evaluation of ARG1 protein ranges revealed a lower on this M2 marker throughout all handled samples, with no vital variations noticed between completely different concentrations or with LY encapsulation (Fig. 6b). Moreover, qRT-PCR evaluation of assorted M1 or M2 markers constantly demonstrated a lower in classical M2 markers comparable to Arg1 and Egr2 (Fig. 6c) and a rise in some M1 markers comparable to Cd86, Il1b, and Il12b (Fig. 6d). Of notice, the addition of LY to the nanoemulsions didn’t result in an enchancment in macrophage reprogramming, which is in slight distinction to what we have now beforehand seen with one other TGF-βR1 inhibitor in human M2-polarized macrophages [56]. We speculated that the potent impact of the VitE:SM automobile was masking the affect of LY in vitro, however we additionally reasoned that the additive impact provided by encapsulating LY within the nanosystems could be extra evident in vivo.
Testing VitE:SM nanoemulsions loaded with the TGF-βR1 inhibitor (LY2157299). a For LY loading, the TGF-βR1 inhibitor was dissolved within the natural part and injected within the aqueous part as beforehand defined (Fig. 1a). VitE:SM = Vitamin E + sphingomyelin nanosystem; VitE:SM:LY = Vitamin E + sphingomyelin + encapsulated TGF-βR1 inhibitor. b Left: Western immunoblot evaluation of ARG1 protein ranges in muBMDMs polarized as in Fig. 2a to M0, M1 or M2 and handled with empty or LY encapsulated VitE:SM nanoemulsions at two completely different concentrations: 1 and 0.5 mg/mL. Proper: Densitometric evaluation of the immunoblots, with the bars representing the imply fold change ± SD (n = 3), with untreated M2 set as 1.0. c Evaluation by qRT-PCR of two M2 markers, Arg1 and Egr2, in the identical samples as described in b. Bars signify the imply fold change ± SD (n = 3), with untreated M2 set as 1.0. d Evaluation by qRT-PCR of M1 markers, Cd86, Il12b and Il1b, in the identical samples as in b and c. Bars signify the imply fold-change ± SD (n = 3), with untreated M1 set as 1.0. ∗ = p < 0.05; ∗ ∗ = p < 0.01; ∗ ∗ ∗ = p < 0.001; ∗ ∗ ∗ ∗ = p < 0.0001; ns not vital. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s put up hoc take a look at, in comparison with M2 in b and c and to M1 in d
In the direction of this finish, C57BL/6 mice had been orthotopically implanted with KPC cells, and VitE:SM:TF or VitE:SM:LY:TF nanoemulsion therapy was initiated on day 4 post-implantation at a dose of 25 mg/kg, administered retro-orbitally each 48 h (3 days per week). Three euthanize time factors to evaluate tumor development had been established: days 21, 28, and 35 post-implantation (Fig. 7a). On the indicated time factors, tumors had been extracted, and a discount in tumor measurement in mice handled with empty nanoemulsions (VitE:SM:TF) and with nanoemulsions loaded with LY (VitE:SM:LY:TF) was noticed (Fig. 7b). Monitoring tumor weight over time revealed that VitE:SM:TF and, extra considerably, VitE:SM:LY:TF exerted a cytostatic impact in comparison with management mice (Fig. 7c). Likewise, the sum of the info throughout all time factors collectively exhibited a major discount in tumor weight in mice handled with each nanoemulsion formulations (Fig. 7c). Histological evaluation of tumor samples revealed the next proportion of tumoral space in mice from the management group, whereas areas of wholesome pancreas had been nonetheless outstanding in lots of mouse pancreata from the therapy teams (Fig. 7d-e).
TGF-βR1 inhibitor (LY2157299)-loaded VitE:SM nanoemulsions scale back tumor development and diminish TAM liver infiltration. a Schematic illustration of the retro-orbital in vivo therapy experiment. C57BL/6 mice had been orthotopically implanted with 2,500 KPC cells/pancreas and retro-orbital therapy (25 mg/kg) was initiated on day 4 post-implantation and administered 3 days per week till the euthanize finish factors: 21, 28, or 35 days post-implantion. b Consultant macroscopic photographs of tumors and adjoining PM for the three teams (Management, VitE:SM:TF and VitE:SM:LY:TF) on the euthanize finish factors: 21, 28, or 35 days post-implantion (DPI). Scale = 1cm. c (Left panel) Weight (g) time course of tumors and adjoining PM from b) on the three experimental finish factors. Three animals per group (n = 3) had been euthanized at 21 and 28 DPI and 4 (n = 4) at 35 DPI. (Proper panel) Fold change in tumor and adjoining PM weight (g) for all animals throughout all the experimental time course. Bars signify the imply fold change ± SD (n = 10), with management set as 1.0. One-way ANOVA take a look at for a number of comparisons with Dunnett’s put up hoc take a look at, in comparison with Management. d Consultant photographs (40X) of H&E-stained tumors from management, VitE:SM:TF- or VitE:SM:LY:TF-treated mice on 35 DPI. T = Tumor, P = Pancreas. Scale = 400µm. e (Left panel) Ratio of the % space of tumor/wholesome pancreas in comparison with the full histologic pancreas/tumor space quantified within the H&E-stained sections from d. One-way ANOVA take a look at for a number of comparisons with Dunnett’s put up hoc take a look at, in comparison with Management set as 1.0. (Proper panel) Frequency of samples from d) categorized based mostly on completely different percentages of tumor/wholesome pancreas as outlined within the legend. f Movement cytometry evaluation of the proportion of CD45 + < CD11b + < F480 + macrophages within the liver samples from c. (Left panel) Time course of macrophage infiltration within the liver on the three euthanize finish factors: 21, 28 or 35 DPI. One-way ANOVA take a look at for a number of comparisons with Dunnett’s put up hoc take a look at, in comparison with Management set as 1.0. (Proper panel) Fold change in liver macrophage infiltration for all animals within the experiment. Bars signify the imply fold-change ± SD (n = 10), with Management set as 1.0. One-way ANOVA take a look at for a number of comparisons with Dunnett’s put up hoc take a look at, in comparison with Management. g Movement cytometry evaluation of the M2 TAM marker CD206. Bars signify the imply fold-change ± SD (n = 10), with Management set as 1.0. One-way ANOVA take a look at for a number of comparisons with Dunnett’s put up hoc take a look at, in comparison with Management. ∗ = p < 0.05; ∗ ∗ = p < 0.01; ∗ ∗ ∗ = p < 0.001; ∗ ∗ ∗ ∗ = p < 0.0001; ns = not vital
Regardless of makes an attempt to detect liver metastases within the orthotopic mannequin, no macroscopic metastases had been discovered on the experimental endpoint (d35) (Determine S7a) in any group, nor did our histological analyses of the liver reveal evident areas of tumor micrometastases (Determine S7b). Since our aim was to focus on liver macrophages within the hope of reprogramming TAMs, livers items had been digested for circulate cytometric evaluation, revealing that not solely did the nanosystems attain the macrophages within the liver (Determine S7c), however a discount within the complete inhabitants of CD45 + /CD11b + /F4/80 + infiltrated macrophages with nanoemulsion remedies was noticed (Fig. 7f). Furthermore, we analyzed the macrophage inhabitants characterised by CD206 expression, a parallel M2 marker for circulate cytometry, and located a major discount in these TAMs with LY encapsulated nanoemulsions (Fig. 7g), reinforcing our goal of M2 TAM focusing on and reprogramming within the liver. Whereas our knowledge help macrophage reprogramming because the mechanism of motion by which the VitE:SM nanoemulsions have an effect on tumor development and TAM liver infiltration, we can’t rule out a doable direct impact on tumor cells; though, circulate cytometry evaluation confirmed a preferential accumulation in macrophages versus the remainder of reside cells (Determine S7d).
To discover the immune profiling and metastasis-related cytokine response induced by nanoparticle therapy, we extracted RNA from liver and tumor tissues and carried out qRT-PCR evaluation on key cytokines. In each the liver (Determine S7e) and tumor (Determine S7f), therapy with VitE:SM, and particularly VitE:SM:LY, led to a major upregulation of pro-inflammatory and Th1-type cytokines (Il12, Tnf, Ptgs2, Cxcl1, Gzmb, and Il6), that are essential for activating immune cells like macrophages and T cells. This pro-inflammatory shift was additional supported by the downregulation of immunosuppressive cytokines (Arg1, Pglyrp1, Ccl2, and Mpo), contributing to a much less permissive setting for metastasis. These findings align with earlier research utilizing Galunisertib LY2157299, which additionally confirmed a shift in direction of a pro-inflammatory, anti-tumor immune response [76]. Moreover, these in vivo outcomes are in keeping with in vitro knowledge detailed above (Figs. 2 and 3), the place VitE:SM and VitE:SM:LY successfully reprogrammed immunosuppressive M2 macrophages right into a pro-inflammatory M0/M1 phenotype.
In distinction to the above detailed in vitro research (Fig. 6), these in vivo outcomes spotlight the synergistic affect of incorporating LY into the VitE:SM nanoemulsions. The outcomes reveal superior outcomes with LY encapsulation in comparison with the effectiveness of VitE:SM nanosystems alone throughout all evaluated parameters, together with tumor development, the proportion of wholesome pancreas in histological samples, and the reprogramming and infiltration of TAMs within the liver. This enhanced efficacy could also be attributed to the physiologically related setting obtained within the in vivo setting the place TGF-β signaling performs an important function in tumor development and TAM recruitment to the liver [16, 17]. This underscored the importance of using the LY-loaded VitE:SM nanoemulsions for our subsequent in vivo PDAC metastasis research.
TGF-βR1 inhibitor (LY2157299)-loaded VitE:SM nanoemulsions diminish liver metastasis in an intrasplenic KPC metastasis mannequin. Whereas the orthotopic mannequin was a superb and biologically-relevant mannequin to check the impact of the nanoemulsions on major tumor development, we concluded that it was not the most suitable choice for assessing liver metastasis, because the development of the first tumor was too speedy and precluded the event of macroscopic liver metastases inside the timeframe of the examine (i.e., earlier than humane endpoint of euthanasia). Consequently, we thought of the feasibility of testing our therapy in a extra acceptable metastasis mannequin. Usually, there are three fashions for finding out PDAC metastasis: intravenous, intraperitoneal, and intrasplenic fashions, generally utilized for investigating lung, peritoneal and lymph node, and liver metastases, respectively [77]. As our goal was to reprogram TAMs within the liver to stop metastasis, the intrasplenic mannequin [55, 78] represented a greater possibility for our nanosystems, as injected cells have direct communication with the liver by the splenic vein (SV). Nevertheless, a pilot experiment was performed to match intrasplenic versus intravenous injection of KPC cells to be able to verify probably the most appropriate mannequin for validating our nanosystems. Per findings within the literature [77], PCR evaluation revealed the next variety of CRE DNA copies (derived from KPC cells) within the liver when utilizing the intrasplenic mannequin. Conversely, the intravenous mannequin emerged as a extra favorable possibility for selling lung colonization (Determine S8).
KPC cells had been injected into the spleens of C57Bl/6 mice, after which cauterization and removing had been carried out to stop the formation of major tumors within the injected organ (Fig. 8a). For these experiments, KPC/mCherry cells had been used to trace tumor cells within the completely different analyzed tissues. Retro-orbital administration of VitE:SM:LY:TF nanoemulsions (25 mg/kg) commenced on day 2 post-intrasplenic injection and was maintained 3 days per week till the experiment’s endpoint on day 18 post-intrasplenic injection (Fig. 8b). Upon euthanasia, we noticed no variations in liver or tumor weight between the management and handled teams (Fig. 8c); nevertheless, macroscopic liver metastases had been detected primarily within the management mice (Fig. 8d and Determine S9). Liver tissue is structured into distinct purposeful models often called lobules, that includes a hexagonal association of portal triads surrounding a central vein and interconnected by sinusoids [79]. In distinction to the handled mice, histological evaluation of livers from management mice revealed lack of hepatocyte microarchitecture, together with a discount within the variety of central veins and sinusoids, indicating tissue disorganization promoted by tumor development (Fig. 8e).
TGF-βR1 inhibitor (LY2157299)-loaded VitE:SM nanoemulsions diminish liver metastasis in an intrasplenic KPC metastasis mannequin. a Schematic of the liver metastasis mannequin involving the injection of KPC/mCherry cells into the spleen earlier than organ resection utilizing a cauterizer (C). L Liver. S Spleen. SV Splenic Vein. b Schematic illustration of the intervention schedules within the liver metastasis mannequin experiment. Spleens had been injected with 25,000 KPC/mCherry cells, and retro-orbital VitE:SM nanoemulsions remedies had been initiated on day 2 post-intrasplenic injection and continued for 16 days, administering three doses (25 mg/kg) per week. c) Weight of the liver (left) or Tumor (T) + adjoining PM (proper) ± SD. Information had been collected from two unbiased experiments; Management (n = 11) and VitE:SM:LY:TF (n = 10). d Consultant macroscopic liver photographs from c. An arrow marks the metastasis within the liver. Scale = 1cm. e Consultant H&E staining from samples obtained from the proper lobe of the liver from d. Scales = 400µm. Zoom areas are depicted inside squares. Scales = 100 µm. CV Central vein, S Sinusoids. f Share of KPC/mCherry cells infiltrated within the liver. Bars signify the imply fold change ± SD, with Management set as 1.0. g Densitometric evaluation of CRE/Gapdh PCR from Determine S8. Murine Gapdh was used as a housekeeping management. Bars signify the imply fold change ± SD, with Management set as 1.0. h Movement cytometry evaluation of the M2 TAM marker CD206 inside the CD11b + < F480 + inhabitants. Bars signify the imply fold change ± SD, with Management set as 1.0. Unpaired t take a look at ∗ = p < 0.05; ∗ ∗ = p < 0.01; ∗ ∗ ∗ = p < 0.001; ∗ ∗ ∗ ∗ = p < 0.0001; ns not vital
On the mobile stage, circulate cytometry evaluation revealed a considerably decrease proportion of KPC/mCherry cells within the livers of handled mice in comparison with controls (Fig. 8f). Moreover, PCR evaluation was carried out to quantify CRE DNA copies (derived from KPC cells) within the liver, displaying a discount in amplification ranges within the livers of handled mice in comparison with management mice (Fig. 8g and S10a). Analyzing the CD206 + TAM inhabitants within the liver by circulate cytometry (CD11b + /F4/80 + /CD206 +), we noticed, in keeping with earlier in vivo knowledge, that the nanosystems reached liver macrophages (Determine S10b) and lowered the CD206 + TAM inhabitants (Fig. 8h). To additional examine the immune profile following therapy, we ready single-cell suspensions from consultant paraffin-embedded livers for FACS evaluation of various immune populations, together with M1/M0 macrophages and T cells. After therapy, we noticed once more a discount in CD206 + M2 macrophages, compensated by a rise in M0/M1 macrophages (Determine S10c). Moreover, there was a rise within the total myeloid inhabitants and CD8 + T cells (Determine S10c), aligning with the proinflammatory cytokine profile seen within the livers of handled mice (Determine S7e). Neutrophils, alternatively, remained unchanged by the therapy (Determine S10c).
With this approximation, we efficiently validated our speculation that reprogramming liver-infiltrating TAMs with the proposed lipid nanosystems has the potential to delay liver metastasis in PDAC. As beforehand talked about, even in circumstances the place the first tumor is successfully resected, roughly 75% of sufferers expertise metastatic relapse inside 5 years post-surgical resection [8,9,10]. Thus, our therapeutic strategy holds promise in stopping liver metastasis relapse for sufferers with resectable major PDAC tumors, and will probably be utilized in mixture with chemotherapeutic interventions in sufferers with metastatic illness. The latter, nevertheless, nonetheless must be examined in experimental fashions.
Ex vivo therapy of human 3D tumor/CAF/macrophage spheroids with VitE:SM nanoemulsions validates the translatability of the nanosystem remedy to people. Lastly, we aimed to determine the translatability of our remedy to the human setting. To realize this aim, we initially remoted and cultured monocyte-derived human macrophages. Subsequently, we induced M2 polarization utilizing MCSF after which uncovered the cells to completely different concentrations of VitE:SM nanoemulsions to judge their impact on M2 macrophage reprogramming. Utilizing the immunosuppressive human TAM markers CD206 and CD163, we noticed that VitE:SM nanoemulsions had been additionally efficient in lowering the M2 inhabitants in vitro (Determine S11a).
Constructing upon this preliminary consequence, we used an ex vivo 3D human spheroid cell mannequin [36] to check the efficacy of our lipid nanoemulsions. On this state of affairs, empty VitE:SM nanoemulsions (with out LY) had been used since no variations in TAM reprogramming had been noticed between VitE:SM or VitE:SM:LY (LY-loaded nanoemulsions) in vitro (Fig. 6b-d). Particularly, we generated in vitro spheroids containing human pancreatic most cancers cells (PANC1), human CAFs, and human macrophages to recreate the PDAC TME in tradition. These spheroids had been handled with VitE:SM nanoemulsions and orthotopically implanted into the pancreas of NOD.SCID mice to evaluate their development and metastasis formation (Fig. 9a). To facilitate their visualization and identification in vivo, PANC1 cells had been contaminated with a GFP-encoding lentivirus, and CAFs with an mCherry-encoding lentivirus. Fluorescence microscopy revealed the spheroid construction, with CAFs/mCherry forming a core surrounded by PANC1/GFP cells, and non-stained macrophages preferentially localizing on the outside of the spheroid (Fig. 9b).
Ex vivo therapy of human 3D tumor/CAF/macrophage spheroids with VitE:SM nanoemulsions. a Schematic of human 3D tumor/CAF/macrophage spheroid technology, illustrating the method of producing human spheroids, comprising three populations of human cells: pancreatic most cancers cells (PANC1), cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and macrophages. The 3D mannequin was created as follows: on day one, PANC1/GFP and CAFs/mCherry had been seeded in wells of a non-adherent plate, and on day 3, macrophages had been added. Spheroids had been handled with VitE:SM nanoemulsions (0.5 mg/mL) on day 4, the medium was modified on day 6, and on day 7, the spheroids had been disaggregated and implanted orthotopically within the NOD.SCID mice. Mice had been monitored for 90 days. b Consultant fluorescence microscopy picture of a human spheroid co-culture. Scale = 1mm. c Schematic illustration of the in vivo orthotopic human spheroid mannequin in NOD.SCID mice. Mice had been euthanized at 90 days post-implantation. d Consultant macroscopic pictures of the tumors on the experimental finish level (90 days post-implantation). S = Spleen served as an anatomical reference for the pancreas. Scale = 1cm. e Bar graph ± SD of tumor weight from d. Information compiled from two unbiased experiments (n = 2) had been normalized, and the management was set as 1.0. Unpaired t take a look at. ∗ = p < 0.05. f Share of GFP + cells (PANC1/GFP) ± SD within the tumor. Information had been normalized for 2 unbiased experiments (n = 2), and the management was set as 1.0. Unpaired t take a look at. ∗ = p < 0.05. g Left: Consultant photographs (40X) of H&E-stained tumor samples from d are proven. T Tumor, P Pancreas. Scale = 400 µm. Proper: Ratio of the % space of tumor/wholesome pancreas ± SD in comparison with the full histologic pancreas/tumor space quantified within the H&E slides from the left panel. Unpaired t take a look at. ns not-significant. h Share of GFP + cells (PANC1/GFP) infiltrated within the liver. Bars signify the imply fold change ± SD, with Management set as 1.0. Unpaired t take a look at. ∗ ∗ ∗ = p < 0.001. .i qRT-PCR evaluation of the ratio of the human GAPDH gene/murine beta actin (mActb). Bars signify the imply fold change ± SD, (n = 2 unbiased experiments), with Management set as 1.0. Unpaired t take a look at. ∗ = p < 0.05
Established spheroids had been both handled (or not) with 1 mg/mL of VitE:SM nanoemulsions, the media was modified 48 h later, and orthotopic implantation of disaggregated spheres was carried out the following day. Implanted NOD.SCID mice had been monitored till day 90 post-implantation (Fig. 9c). Upon euthanasia, we noticed a discount within the major tumor burden in mice implanted with VitE:SM handled in comparison with untreated spheroids (Fig. 9d and Determine S11b), which we confirmed on the stage of pancreatic/tumor weight (Fig. 9e). Movement cytometry evaluation of cells extracted from digested tumors additionally revealed a discount within the share of PANC1/GFP cells in tumors generated from handled spheroids (Fig. 9f). Histological evaluation of those tumors confirmed the next proportion of tumoral space in management tumors versus tumors generated from handled spheroids, the place areas of wholesome pancreas had been clearly seen (Fig. 9g). On the stage of metastases, we didn’t detect macroscopic liver metastases in both management or handled mice (Determine S11c). Nevertheless, on the mobile stage, we discovered that mice implanted with handled spheroids had a major discount in PANC1/GFP cells within the liver in comparison with controls, decided by circulate cytometry (Fig. 9h). To verify this consequence, we carried out qRT-PCR for the human GAPDH gene to find out the presence of cells of human origin within the liver. Consistent with our circulate cytometric analyses, we detected decrease amplification of GAPDH in mice implanted with handled spheroids in comparison with mice implanted with non-treated spheroids (Fig. 9i).
To validate that the consequences noticed had been on the macrophage stage, a parallel experiment excluding macrophages from the PANC1/GFP:CAFs/mCherry spheroids was carried out. Spheroids devoid of macrophages had been handled with VitE:SM nanoemulsions underneath the identical situations because the earlier experiment, orthotopically implanted in NOD.SCID mice, and euthanized on day 90 post-implantation (Determine S12a). Upon evaluation, we noticed no vital discount in tumor weight (Determine S12b-c) nor within the stage of liver metastasis. Importantly, the evaluation of the liver revealed no vital lower within the share of PANC1/GFP cells nor within the stage of human GAPDH between the 2 experimental teams (Determine S12d-e). As such, and in step with the ultimate conclusions decided within the murine system, these findings help the principle conclusion that the effectiveness of the nanoemulsions remedy depends on focusing on/repolarizing macrophages.
It is very important level out that the human mannequin utilized herein has its limitations. Firstly, immunocompromised NOD.SCID mice, which have impaired macrophage perform, had been utilized for the engraftment of human cells in vivo. Secondly, human macrophages had been pre-treated previous to injection. Thirdly, mice weren’t handled with the nanosystems put up orthotopic implantation. Thus, whereas the strategy doesn’t faithfully recapitulate the metastatic setting/cascade nor a therapeutic intervention strategy, these findings do provide promising preliminary help for the doable translatability of a VitE:SM-based lipid nanoemulsions remedy for human PDAC. Furthermore, the outcomes once more spotlight the pivotal function of macrophages because the mediators of the therapeutic impact of this nanosystem. Whereas a totally humanized mouse mannequin with human macrophages would have been a extra best in vivo mannequin, the demonstrated effectiveness of our lipid nanosystem remedy on this mannequin of human pancreatic most cancers reinforces the idea {that a} novel nanosystem, which additionally capabilities as a drug supply system, holds the potential to scale back tumor development and stop liver metastasis for PDAC sufferers.